Quantum Computing Explained in a Simple Way
Quantum computing sounds like one of those sci-fi terms that feels far from daily life. But honestly, it is already moving faster than most people realize. Big tech companies, research labs, and even governments are investing heavily because this technology can change how we solve problems that classical computers struggle with.
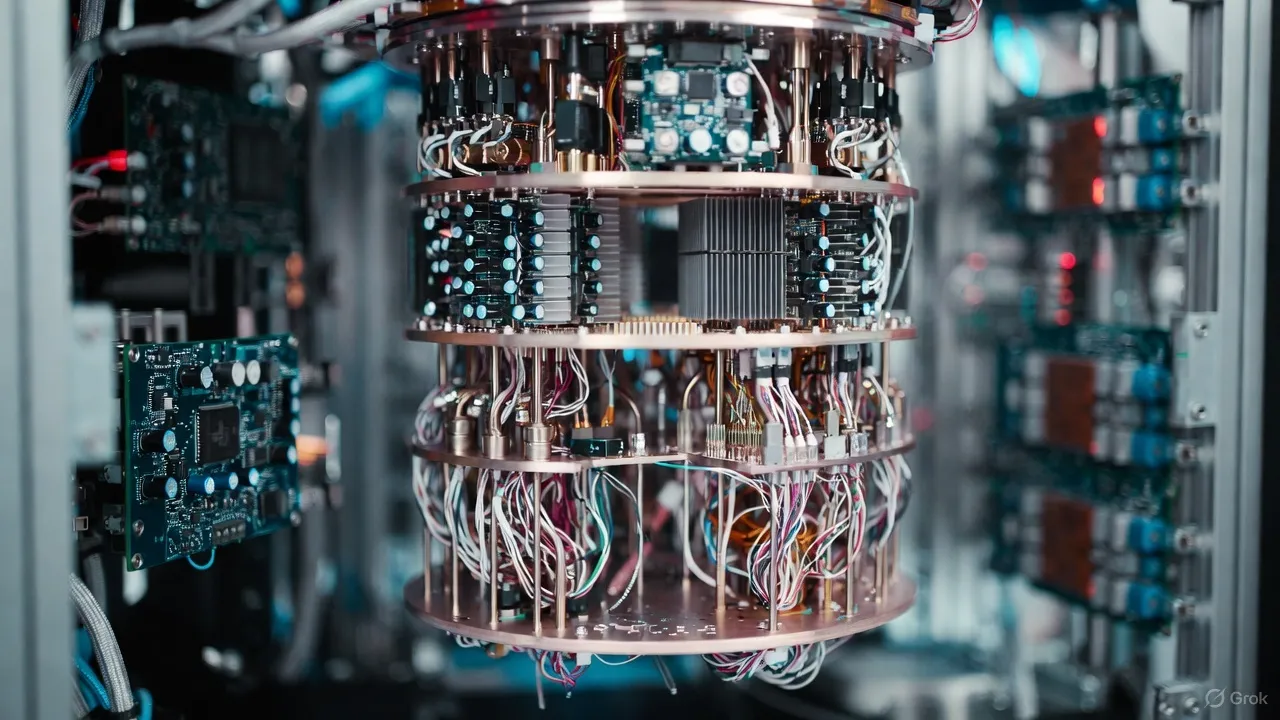
Let us first clear the basics.
What Is Quantum Computing
Traditional computers work with bits. A bit is either 0 or 1. Quantum computers use qubits. A qubit can be 0, 1, or both at the same time due to a concept called superposition. It feels confusing at first, yeah, but this ability allows quantum systems to process many possibilities simultaneously.
Another key idea is entanglement. When qubits are entangled, the state of one instantly affects the other, even if they are far apart. This gives quantum computers a massive advantage in certain types of calculations.
Why Quantum Computing Is So Powerful
Quantum computers are not meant to replace your laptop or phone. They are designed for very specific, complex tasks. Problems like optimizing logistics routes, simulating molecules for drug discovery, cracking complex encryption, and modeling climate systems.
For example, simulating molecules at a quantum level is extremely hard for classical computers. Quantum computers handle this naturally, because nature itself works on quantum rules. That is the big deal here.
Real World Use Cases Today
Quantum computing is not just theory anymore. Companies are already testing real applications.
In healthcare, quantum systems help researchers simulate chemical reactions faster, which can speed up drug discovery. In finance, they are used to optimize portfolios and assess risk under countless variables. In cybersecurity, quantum computing is forcing a rethink of encryption standards, because future quantum machines could break today’s security methods.
Not everything is ready yet, but progress is steady. Some days slow, some days surprisingly fast.
Challenges Still Holding It Back
Quantum computers are fragile. Qubits are sensitive to temperature, vibration, and even tiny environmental noise. Maintaining stability is one of the biggest challenges.
Another issue is error correction. Quantum errors happen more often than classical ones, and fixing them requires more qubits, which increases complexity. So yes, we are not at mass adoption stage yet.
Still, the momentum is real.
Why Quantum Computing Matters for the Future
Quantum computing has the potential to reshape industries the way the internet once did. It will not affect everyone overnight, but when it matures, its impact will be deep and long lasting.
Governments, universities, and companies like Google, IBM, and Microsoft are pushing research forward. That alone shows how important this field has become.
In simple words, quantum computing is not about faster emails or better games. It is about solving problems we could never solve before. And that is why it matters so much right now.
If you are watching future tech trends, this is one space you really should not ignore.